- Home
- About Doctor
- For Patients
- Gall Stones
- Appendicitis Treatments
- Obesity
- Oesophagus Cancer
- Gastric Ulcers And Treatments
- Duodenal Ulcers
- Stomach Cancer
- Liver Diseases
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Pancreatitis diseases and tumours of the pancreas
- Perforation of the intestine
- Abdominal Trauma
- Jaundice Treatment
- Crohn’s Disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Colon Polyps
- Hernia
- Piles
- Cancers
- Fissure
- Fistula
- Thyroid Disorders
- Swelling and Abscesses anywhere in The Body
- Surgeries Offered
- Gastrointestinal Surgeries
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Surgery for GERD
- Trauma Surgery
- Surgeries for Obstructive Jaundice
- Surgeries for the Pancreas
- Surgeries on the Stomach
- Bariatric Surgery
- Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastronomy
- Hernia Surgery
- Breast Surgery
- Small and Large Intestine Surgeries
- Colorectal Surgery
- Testimonials
- Blogs
- FAQs
- News And Events
- Gallery
- Contact Us
- Book an Appointment
Let’s understand all about Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal Obstruction is the blockage of the intestine that inhibits the normal passage of food and bowels through it. It is commonly called bowel obstruction. The problem may occur either in the small or large intestine. In the natural process, the food moves from the stomach to the intestine wherein it is broken down into smaller parts and absorbed or eliminated as stools. This sequence is interrupted when there is a blockage.
The blockage may be partial or complete. Sometimes, there may be a pseudo-obstruction wherein the symptoms of bowel blockage are experienced without any actual physical barriers in the intestinal organs. This occurs due to the weakening of gastrointestinal muscles or nerves that control them. Patients suffering from this disorder need medical attention especially if they have a complete obstruction. Chennai Gastro Care is a prominent institute that offers comprehensive treatment for such gastroenterology problems. It is supported by a highly skilled and experienced team of gastro doctors in Chennai who specialize in addressing various issues of the digestive tract with promising outcomes.
Causes
- Abdominal adhesions or tissue growth
- Volvulus (twisting of the intestine)
- Narrowing of the intestine due to intussusception
- Perforation of the intestine
- Scarring due to surgery, infection or tearing of the abdominal wall
- Damaged blood vessels in the abdominal walls
- Tumours(both benign and malignant)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Diverticulitis in which tiny pouches grow in the intestinal lining
- Presence of foreign(non-edible) objects
Patients suffering from Hernia, Crohn’s Disease, various types of cancer including colon cancer, stomach cancer or ovarian cancer or who have undergone abdominal radiation treatment are at greater risk of getting intestinal obstructions.
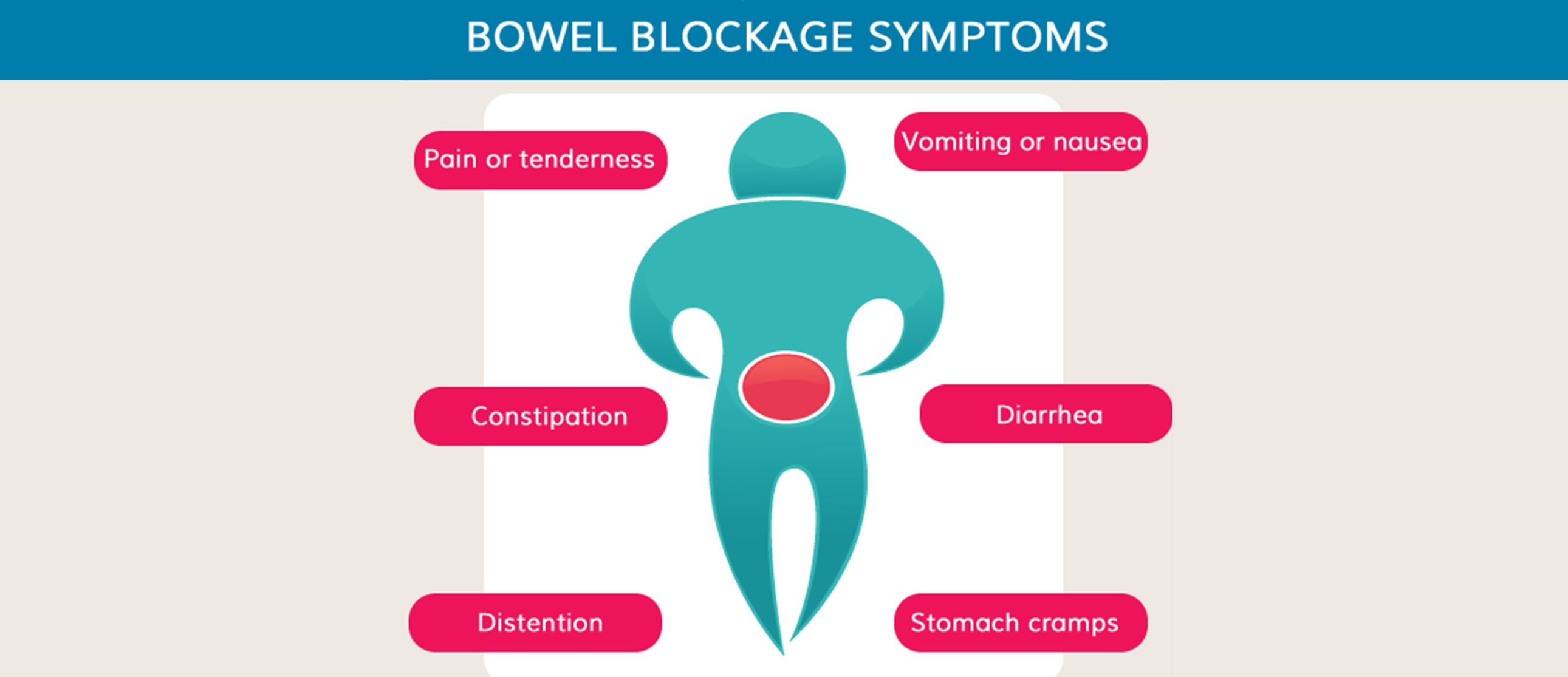
Symptoms
- Severe abdominal pain
- Cramping sensation in the stomach
- Vomiting episodes
- Unusual feeling of satiety
- Swelling of the abdominal region
- Loud sounds from the abdomen
- Accumulation of gas in the stomach and discomfort
- Constipation
- Lack of appetite
- Diarrhoea(in case of partial blockage)
Diagnosis
The intestinal obstruction is detected by physical examination and various diagnostic tests like x-ray, CT scan, ultrasound scan and air or barium enema (for enhanced imaging of the colon).
Treatment
The type of treatment is based on the cause of obstruction but in most cases it requires hospitalization.
- Stabilization-The patient must be stabilized before actual treatment begins. For this they may be administered intravenous fluids, relieved from abdominal bloating by the suction of fluid and air and catheterized to remove the urine in the bladder.
- Barium/Air Enema-This process is mainly used to treat children who suffer from intussusception. If the enema can clear the blockage, further medical intervention may not be required.
- • Partial Obstruction-In this case, first the stabilization procedure is done and a low-fibre diet is recommended so that the food may be easily processed by the partially blocked intestine. If this approach does not clear the blockage, surgery may be inevitable.
- Complete Obstruction-When there is no passage of food and fluids through the intestine, surgery must be done to relieve the symptoms. The kind of small and large intestine surgeries depends on the affected portion and type of blockage. Usually, both the blockage and the damaged tissues are removed. Sometimes, a self-expanding stent is placed by the endoscopic method to forcefully open the colon and clear the barrier. This method is usually used for colon cancer patients as they cannot withstand emergency surgery. However, surgery may be needed subsequently after stabilization as the stent only provides temporary relief.
- Pseudo Obstruction-If the symptoms are caused by a pseudo-obstruction (also termed paralytic ileus), the patient may be admitted for a short duration and given food through a nasal tube or intravenous fluids to avoid malnutrition. Medications are prescribed to improve muscle contractions. Doing this improves the flow of food and fluids through the intestine and eases the bowel movements. Any underlying condition causing the obstruction is treated appropriately and other medicines causing the problem are eliminated.
- Decompression-For the enlargement of the colon, an intervention called decompression is beneficial. In this procedure, a thin tube is inserted into the colon through the anus by colonoscopy. Alternatively, decompression may also be done by surgery.
Prevention
The risk of developing intestinal obstruction may be reduced by eating small quantities of a low-fat balanced diet enriched with vegetables and fruits frequently, remaining well-hydrated and avoiding smoking.
Ask doctor
Testimonials
 Very practical approach to my dads gallbladder stone problem .. Surgery was explained well by diagrams and he performed the surgery by key holes which made it pain free for my dad . I had consulted many in the last 1 month including
Very practical approach to my dads gallbladder stone problem .. Surgery was explained well by diagrams and he performed the surgery by key holes which made it pain free for my dad . I had consulted many in the last 1 month including 
Subramanian
Read More The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger
The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger 
Mehul Kain
Read More The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger
The doctor was helpful. He worked with me to select the best option for treatment and helped finalize treatment. He ensured that my appointment went ahead as planned and followed up rigorously post op too. Scar was a bit larger 


